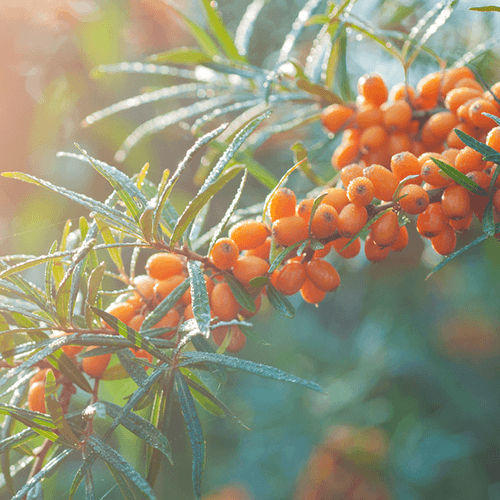
Sea buckthorn
Scientific names: Hippophae rhamnoides
Family: Elaeagnaceae
Alternative names: Ananas de Sibérie, Argasse, Argousier, Argousier Faux-Nerprun, Bourdaine Marine, Buckthorn, Chharma, Dhar-Bu, Épine Luisante, Épine Marrante, Espino Armarillo, Espino Falso, Faux Nerprun, Finbar, Grisset, Meerdorn, Oblepikha, Olivier de Sibérie, Purging Thorn, Rokitnik, Sallow Thorn, Sanddorn, Saule Épineux, Sceitbezien, Sea-Buckthorn, Seedorn, Star-Bu, Tindved, White Sea Buckthorn
Actions: Anticancer, Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, Blood pressure, Cardiovascular, Coagulation, Cold stress reduction, Dermatologic, Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, Immunomodulatory, Ocular, Radioprotective, Wound-healing
Background
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) is a plant found throughout Europe and Asia. The leaves, flowers, seeds, and fruits are used as medicine.
Sea buckthorn contains vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and C, as well as other active ingredients. It's been used traditionally to slow down the aging process.
People use sea buckthorn for burns, eczema, acne, indigestion, high blood pressure, wrinkled skin, and many other purposes, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of uses.
Don't confuse sea buckthorn with other plants known as "buckthorn," including alder buckthorn, European buckthorn, and Cascara sagrada. These are not the same.
Sea buckthorn contains vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and C, as well as other active ingredients. It's been used traditionally to slow down the aging process.
People use sea buckthorn for burns, eczema, acne, indigestion, high blood pressure, wrinkled skin, and many other purposes, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of uses.
Don't confuse sea buckthorn with other plants known as "buckthorn," including alder buckthorn, European buckthorn, and Cascara sagrada. These are not the same.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Sea buckthorn fruit is commonly consumed as food. Sea buckthorn fruit is used in jams, pies, drinks, and other foods. The oil extract of sea buckthorn fruit and seed is possibly safe when used for up to 90 days. There isn't enough reliable information to know if sea buckthorn leaf or leaf extracts are safe or what the side effects might be.
When applied to the skin: Sea buckthorn fruit is possibly safe when used in a cream for up to 13 days. It might cause red or itchy skin for some people.
Children: Sea buckthorn is possibly safe when taken by mouth for up to 8 weeks in children 1-7 years of age.
Bleeding disorder: Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting when taken as a medicine. It might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding in people with bleeding disorders.
Surgery: Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting when taken as a medicine. It might cause extra bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using sea buckthorn at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
When applied to the skin: Sea buckthorn fruit is possibly safe when used in a cream for up to 13 days. It might cause red or itchy skin for some people.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if sea buckthorn is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and stick to food amounts.Children: Sea buckthorn is possibly safe when taken by mouth for up to 8 weeks in children 1-7 years of age.
Bleeding disorder: Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting when taken as a medicine. It might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding in people with bleeding disorders.
Surgery: Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting when taken as a medicine. It might cause extra bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using sea buckthorn at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Effectiveness
NatMed Pro rates effectiveness based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Effective, Likely Effective, Possibly Effective, Possibly Ineffective, Likely Ineffective, Ineffective, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate.
Possibly effective Effectiveness definitions
- Burns. Applying a sea buckthorn cream seems to help burns heal faster.
Possibly ineffective Effectiveness definitions
- Eczema (atopic dermatitis). Neither taking sea buckthorn by mouth nor applying a sea buckthorn cream to the skin seems to help eczema.
Dosing & administration
Sea buckthorn has been used in extracts, fruit purees, seed oils, pulp oils, creams, and sprays. There isn't enough reliable information to know what an appropriate dose of sea buckthorn might be. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult a healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Medications for high blood pressure (Antihypertensive drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Sea buckthorn might lower blood pressure. Taking sea buckthorn along with medications that lower blood pressure might cause blood pressure to go too low. Monitor your blood pressure closely.
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting. Taking sea buckthorn along with medications that also slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood pressure: Sea buckthorn might lower blood pressure. Taking it with other supplements that have the same effect might cause blood pressure to drop too much. Examples of supplements with this effect include andrographis, casein peptides, L-arginine, niacin, and stinging nettle.
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginger, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Sea buckthorn might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginger, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Interactions with foods
There are no known interactions with foods.
Products
View all productsPractitioner product
Practitioner product
RRP: $50.50$35.35Save: 30%
Create account
Practitioner product
RRP: $65.95$56.06Save: 15%
Create account
Per 6 g:
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Hydrolysed collagen
- Camellia sinensis 1.32 g
- Inulin (Dietary fibre)
- Pouteria lucuma (fruit) powder
- Coconut medium-chain triglyceride (Coconut MCT)
- Natural vanilla flavour
- Siraitia grosvenorii (Monk fruit)
RRP: $34.95$29.71Save: 15%
Create account
Per 9 g:
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Chlorella pyrenoidosa powder
- Brassica oleracea var. acephala (leaf) powder (Kale)
- Inulin (Dietary fibre)
- Medicago sativa
- Brassica oleracea var. italica (Broccoli)
- Spinacia oleracea (Spinach)
- Green banana
- Bacillus coagulans (GBI-30)
- Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina)
- Laminaria digitara (Kelp)
- Euterpe oleracea (berry) ext. (Acai)
- Vaccinium corymbosum
- Malpighia glabra
- Beta vulgaris
- Punica granatum juice dry
- Lycium chinese
- Golden pea protein (sprout) bio-fermented
- Apple pectin
- Rubus idaeus (berry)
- Fragaria ananassa (Strawberry)
- Lycopersicon esculentum
- Arctic sea algae
- Sea salt
- Sunflower seed extract
- Ananas comosus (Pineapple)
- Citrus limon (Lemon)
- Linum usitatissimum (seed) (Flaxseed)
- Malus (Apple)
- Lepidium meyenii
- Natural flavours
- Silybum marianum
- Equisetum arvense
- Centella asiatica
- Glycyrrhiza glabra (root)
- Althaea officinalis (root)
- Melissa officinalis
- Taraxacum officinale (leaf)
- Zingiber officinale (root)
- Withania somnifera
- Aloe barbadensis (leaf)
- Panax ginseng
- Pumpkin powder
- Sweet potato powder
- Sunflower seed
- Vaccinium macrocarpon
- Grifola frondosa (mushroom)
- Lentinula edodes (mushroom)
- Myrciaria dubia (fruit) powder (Camu Camu)
- Protease
- Amylase enzyme
- Lipase
- Cellulase
- Lactase
- Mesquite (pod) powder
- Thaumatin
- Prunus salicina (Queen Garnet plum)
- Chlorella pyrenoidosa powder
RRP: $139.95$118.97Save: 15%
Create account
Per 12 g serve (Blueberry Wildflower):
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn) juice
- Hydrolysed bovine collagen peptides
- Bovine collagen peptides 3 g
- Citrus aurantiifolia (Lime)
- Beta vulgaris (root) powder (Beetroot)
- Siraitia grosvenorii (Monk fruit)
- Viola odorata
- Matcha butterfly pea blend flower
- Sambucus nigra
- Vaccinium corymbosum (fruit) powder
- Rubus idaeus
- Natural flavours
- Bambusa breviflora (stem) ext. dry
- Psidium guajava (leaf) ext.
225 g Blueberry Wildflower
RRP: $49.50$42.08Save: 15%
Create account
Per 30 g (Vanilla Maple):
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn) juice
- Golden pea protein
- Marine collagen peptides
- Natural flavours
- Amylase enzyme
- Protease
- Lipase
- Cellulase
- Stevia rebaubiana (leaf) ext.
- Siraitia grosvenorii (Monk fruit)
- Lactase
RRP: $51.00$40.80Save: 20%
OOS at supplier
Create account
return unknown
Per 5 g:
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Fragaria ananassa (Strawberry)
- Euterpe oleracea (berry) ext. (Acai)
- Vaccinium corymbosum (fruit) powder
- Vaccinium macrocarpon
- Mango (fruit)
- Beta vulgaris (root) powder (Beetroot)
- Pouteria lucuma (fruit) powder
- Oryza sativa (Rice)
- Curry leaf extract
- Psidium guajava (Guava)
- Oryza sativa (Rice fibre)
- Natural flavours
- Bambusa arundinacea (stem)
- Agaricus bisporus
RRP: $44.95$38.20Save: 15%
Create account
RRP: $69.95$59.46Save: 15%
Create account
Per 4 g:
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn) powder
- Terminalia ferdinandiana
- Davidson plum powder
- Marine collagen peptides
- Green banana
- Berry flavour
- Lycopersicon esculentum powder
- Sesamum indicum
- Daucus carota powder
- Bambusa arundinacea
- Sesbania sp.
- Tocotrienols (Vitamin E)
- Santalum acuminatum
$69.95
Currently unavailable at vital.ly
Create account
Per 67 g (Blueberry):
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Bovine gelatin
- Vaccinium corymbosum
- Malus (Apple)
- Nature identical flavours
- Blue spirulina
- Thaumatin
RRP: $22.95$19.51Save: 15%
Create account
Per 10 g
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Theobroma cacao (Cocoa powder) 5.5 g
- Magnesium
- Hydrolysed collagen
- Ceratonia siliqua (pod) powder (Carob)
- Natural vanilla flavour
- Coconut medium-chain triglyceride (Coconut MCT)
- Siraitia grosvenorii (Monk fruit)
- Thaumatin
- Pink Himalayan crystal salt
RRP: $29.95$25.46Save: 15%
Create account
Per 11 g:
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Golden pea protein (sprout) bio-fermented
- Medicago sativa
- Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina)
- Brassica oleracea var. acephala (leaf) powder (Kale)
- Chlorella vulgaris
- Brassica oleracea var. italica
- Spinacia oleracea
- Laminaria digitara (Kelp)
- Vaccinium corymbosum
- Fragaria ananassa (Strawberry)
- Euterpe oleracea (berry) ext. (Acai)
- Rubus idaeus
- Punica granatum
- Beta vulgaris
- Lycium barbarum
- Malpighia glabra
- Lycopersicon esculentum (Tomato)
- Natural flavours
- Inulin (Dietary fibre)
- Apple pectin
- Green banana starch
- Bacillus coagulans (GBI-30)
- Arctic sea algae
- Sea salt
- Linum usitatissimum (seed) (Flaxseed)
- Citrus limon (Lemon)
- Sunflower seed extract
- Ananas comosus (Pineapple)
- Malus (Apple)
- Lepidium meyenii
- Silybum marianum
- Centella asiatica
- Glycyrrhiza spp. (root)
- Althaea officinalis (root)
- Melissa officinalis
- Taraxacum officinale (leaf)
- Zingiber officinale (root)
- Aloe barbadensis (leaf)
- Panax ginseng
- Pumpkin powder
- Sweet potato powder
- Vaccinium macrocarpon
- Grifola frondosa
- Lentinula edodes
- Myrciaria dubia (fruit) powder (Camu Camu)
- Protease
- Amylase enzyme
- Lipase
- Cellulase
- Lactase
- Mesquite (pod) powder
- Thaumatin
RRP: $84.95$72.22Save: 15%
Create account
Per capsule:
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn) powder
- Terminalia ferdinandiana
- Davidson plum powder
- Marine collagen peptides
- Santalum acuminatum
- Green banana
- Berry flavour
- Lycopersicon esculentum
- Sesamum indicum
- Daucus carota powder
- Bambusa arundinacea
- Sesbania sp.
- Tocotrienols (Vitamin E)
RRP: $69.95$55.96Save: 20%
Create account
Per 5 g (Unflavoured):
- Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
- Green banana starch
- Inulin (Dietary fibre)
- Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (Partially hydrolysed guar gum (PHGG))
- Apple pectin
- Fructooligosaccharides
- Arctic sea algae
- Protease
- Amylase enzyme
- Lipase
- Cellulase
- Lactase
- Curcumin (Turmeric)
- Zingiber officinale
- Melissa officinalis
- Glycyrrhiza glabra (root)
- Bacillus coagulans (GBI-30)
- Psidium guajava (leaf)
- Vitis vinifera
- Thaumatin
RRP: $44.95$38.20Save: 15%
Discontinued by Nutra Organics
Create account
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 18/07/2025 10:00:00 and last updated on 21/03/2018 19:15:40. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.