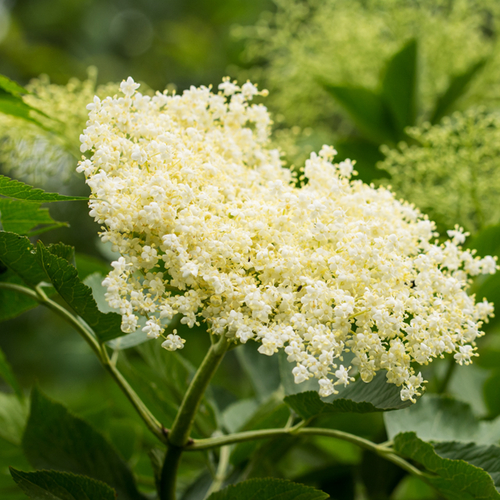
Elderflower
Scientific names: Sambucus nigra
Family: Adoxaceae/Sambucaceae
Alternate names: Arbre de Judas, Black-Berried Alder, Black Elder, Boor Tree, Bountry, Common Elder, Ellanwood, Ellhorn, European Alder, European Black Elder, European Black Elderflower, European Elderflower, European Elder Flower, Fleur de Sureau, Fleur de Sureau Noir, Flor de Saúco, Flos Sambuci, Hautbois, Haut Bois, Sambuc, Sambucus, Sambucus Flos, Sambucus Nigra Flos, Seuillon, Sureau Commun, Sureau Noir, Sussier, Sweet Elder
Background
Elderflower is the flower of the European or black elder tree (Sambucus nigra), which is also the source of elderberry. Its flower is used as medicine.
Elderflower contains chemicals that have antioxidant effects. It also contains chemicals that might have antidiabetic effects.
People use elderflower for common cold, constipation, diabetes, obesity, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Don't confuse elderflower with American elder, dwarf elder, or elderberry. These are not the same.
Elderflower contains chemicals that have antioxidant effects. It also contains chemicals that might have antidiabetic effects.
People use elderflower for common cold, constipation, diabetes, obesity, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Don't confuse elderflower with American elder, dwarf elder, or elderberry. These are not the same.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Elderflower is commonly consumed in foods. Dried elderflower is possibly safe when used in doses of 3.9 grams daily for 8 days, or in small amounts as part of a specific combination product containing elderflower, sorrel, gentian root, verbena, and cowslip flower (SinuComp, Phytopharmica) for up to 14 days. But elderflower is possibly unsafe when used in excessive amounts. Some parts of the elder tree contain a toxin that can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough relatable information to know if elderflower is safe or what the side effects might be.
Surgery: Elderflower might lower blood sugar levels. This might interfere with blood sugar control during and after surgery. Stop using elderflower at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough relatable information to know if elderflower is safe or what the side effects might be.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if elderflower is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.Surgery: Elderflower might lower blood sugar levels. This might interfere with blood sugar control during and after surgery. Stop using elderflower at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Effectiveness
Effective Effectiveness definitions
There is interest in using elderflower for a number of purposes, but there isn't enough reliable information to say whether it might be helpful.
Dosing & administration
There isn't enough reliable information to know what an appropriate dose of elderflower might be. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult a healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Elderflower might lower blood sugar levels. Taking elderflower along with diabetes medications might cause blood sugar to drop too low. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar: Elderflower might lower blood sugar. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might lower blood sugar too much. Examples of supplements with this effect include aloe, bitter melon, cassia cinnamon, chromium, and prickly pear cactus.
Interactions with foods
There are no known interactions with foods.
Products
View all productsPer 5 g (Watermelon & Berry):
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Per capsule:
RRP: $36.60$30.37Save: 17%
Create account
Per 10 mL:
- Sambucus nigra (Elderflower) ext. equiv. dry 2.1 g
- Euphrasia officinalis ext. equiv. dry 1.05 g
- Echinacea purpurea ext. equiv. dry 1.05 g
- Plantago lanceolata ext. equiv. dry 840 mg
- Achillea millefolium ext. equiv. dry 700 mg
- Tilia cordata ext. equiv. dry 700 mg
- Calendula officinalis ext. equiv. dry 420 mg
- Cinnamomum verum ext. equiv. dry 210 mg
- Pimpinella anisum (seed) oil
- Water
- Glycerol
- Alcohol
Practitioner product
RRP: $69.95$59.46Save: 15%
Create account
Per serve (Blueberry Wildflower):
- Sambucus nigra (Elderflower)
- Hydrolysed bovine collagen peptides
- Bovine collagen peptides 3 g
- Citrus aurantiifolia (Lime)
- Beta vulgaris (root) powder (Beetroot)
- Siraitia grosvenorii (Monk fruit)
- Viola odorata
- Matcha butterfly pea blend flower
- Vaccinium corymbosum (fruit) powder
- Rubus idaeus
- Natural flavours
- Hippophae rhamnoides juice
- Bambusa breviflora (stem) ext. dry
- Psidium guajava (leaf) ext.
225 g Blueberry Wildflower
RRP: $49.50$42.08Save: 15%
Create account
Per 3 g:
- Sambucus nigra (Elderberry) (fruit)
- Sambucus nigra (Elderflower)
- Echinacea angustifolia
- Astragalus membranaceus
- Lycium barbarum
- Rosa canina
- Luo Han Guo (fruit) ext. (Monk fruit)
- Echinacea purpurea
- Glycyrrhiza glabra (root)
- Olea europaea (leaf)
- Calendula officinalis
- Origanum vulgare
- Uncaria tomentosa
- Mentha x piperita
- Thymus vulgaris
- Cola acuminata
- Foeniculum vulgare
- Inula helenium
- Asclepias tuberosa
- Achillea millefolium
- Armoracia rusticana
- Capsicum spp.
- Allium sativum
- Allium cepa
- Zingiber officinale
- Cordyceps sinensis (mushroom)
- Ganoderma lucidum (mushroom)
- Lentinula edodes (mushroom)
- Tremella fuciformis (mushroom)
- Trametes versicolor (mushroom)
- Salvia eremostachya
- Hericium erinaceus (mushroom)
- Inonotus obliquus (mushroom)
- Ilex paraguariensis
RRP: $49.95$47.45Save: 5%
Create account
Per tea bag:
RRP: $10.25$9.43Save: 8%
Create account
Per 2.5 mL:
RRP: $28.95$24.61Save: 15%
OOS at supplier
Create account
return unknown
Per 1 mL:
- Sambucus nigra (Elderflower) ext. 41.7 mg
- Echinacea purpurea ext. 6.7 mg
- Leptospermum scoparium (Manuka honey) 65 mg
- Euphrasia
- Beta-carotene carotenoids (Vitamin A) 150 μg equiv. vitamin A RE 25 μg
- Cholecalciferol 0.25 μg equiv. vitamin D3 10 IU
- Zinc glycinate 443 μg equiv. zinc 125 μg
- Mentha x piperita ext. 13.3 mg
- Hedera helix ext. 5 mg
- Honey 325 mg
- Gelsemium sempervirens
- Sodium chloride (Nat mur)
- Anemone pulsatilla (Pasque flower)
- Allium cepa 3 C
RRP: $20.99$16.79Save: 20%
Discontinued by Brauer
Create account
Per 1 mL:
- Sambucus nigra (Elderflower) ext. 41.7 mg
- Althaea officinalis ext. 50 mg
- Leptospermum scoparium (Manuka honey) 60 mg
- Beta-carotene carotenoids (Vitamin A) 150 μg equiv. vitamin A RE 25 μg
- Cholecalciferol 0.216 μg equiv. vitamin D3 8.6 IU
- Zinc glycinate 416 μg equiv. zinc 127 μg
- Honey 250 mg
- Bryonia alba
- Rumex crispus
RRP: $20.99$16.79Save: 20%
Discontinued by Brauer
Create account
Per 1 mL:
- Sambucus nigra (Elderflower) ext. 22.22 mg
- Euphrasia
- Pulsatilla pratensis
- Echinacea purpurea ext. 13.34 mg
- Zinc glycinate 670 μg equiv. zinc 200 μg
- Calcium ascorbate dihydrate (Vitamin C) 24.33 mg equiv. ascorbic acid 20 mg
- Gelsemium sempervirens
- Rhus toxicodendron (Poison Ivy)
- Mentha x piperita ext. 13.33 mg
- Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) 0.25 μg equiv. vitamin D 10 IU
- Allium cepa (Onion)
RRP: $20.99$16.79Save: 20%
Discontinued by Brauer
Create account
RRP: $29.95$25.47Save: 15%
OOS at supplier
Create account
return unknown
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 17/12/2024 11:00:00 and last updated on 23/10/2020 01:46:55. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.