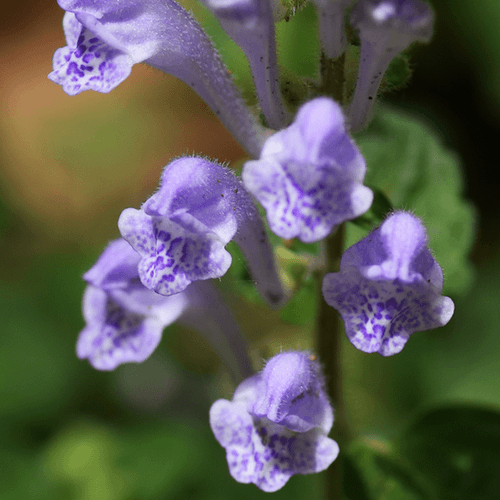
Background
Baikal skullcap contains chemicals that might decrease swelling and stop tumor growth.
Baikal skullcap is used for respiratory infections, diabetes, osteoarthritis, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support any uses. There is also no good evidence to support using Baikal skullcap for COVID-19.
Don't confuse Baikal skullcap with skullcap. They are different plants.
Safety Safety definitions
One specific product (Limbrel, Primus Pharmaceuticals) has been linked to serious side effects. It contains a mixture of Baikal skullcap and catechu. There have been multiple reports of liver and lung injury with this product. In 2017, the US FDA recalled this product due to serious safety concerns. It's unclear if these concerns are due to Baikal skullcap, catechu, or the combination.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough reliable information to know if Baikal skullcap is safe or what the side effects might be.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if Baikal skullcap is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.Bleeding disorders. Baikal skullcap might slow blood clotting. In theory, Baikal skullcap might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding in people with bleeding disorders.
Hormone-sensitive condition such as breast cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, endometriosis, or uterine fibroids: Baikal skullcap might have the same effects as estrogen. If you have any condition that might be made worse by estrogen, don't use Baikal skullcap.
Surgery: Baikal skullcap might slow blood clotting. It might cause extra bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using Baikal skullcap at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Effectiveness
Dosing & administration
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Alcohol (Ethanol)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Alcohol can cause sleepiness and drowsiness. Baikal skullcap might also cause sleepiness and drowsiness. Taking large amounts of Baikal skullcap along with alcohol might cause too much sleepiness.
Estrogens
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Baikal skullcap might have some of the same effects as estrogen. Taking Baikal skullcap along with estrogen pills might decrease the effects of estrogen pills.
Lithium
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Taking Baikal skullcap might decrease how well the body gets rid of lithium. This could increase how much lithium is in the body and result in serious side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider before using this product if you are taking lithium. Your lithium dose might need to be changed.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Baikal skullcap might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Baikal skullcap might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications for an overactive thyroid (Antithyroid drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Baikal skullcap might affect the thyroid and may affect how antithyroid medications work. Do not take Baikal skullcap if you are taking medications for an overactive thyroid.
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Baikal skullcap might lower blood sugar levels. Taking Baikal skullcap along with diabetes medications might cause blood sugar to drop too low. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
Medications for high blood pressure (Antihypertensive drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Baikal skullcap might lower blood pressure. Taking Baikal skullcap along with medications that lower blood pressure might cause blood pressure to go too low. Monitor your blood pressure closely.
Medications moved by pumps in cells (Organic anion-transporting polypeptide substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are moved in and out of cells by pumps. Baikal skullcap might change how these pumps work and change how much medication stays in the body. In some cases, this might change the effects and side effects of a medication.
Medications moved by pumps in cells (P-glycoprotein substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are moved in and out of cells by pumps. Baikal skullcap might change how these pumps work and change how much medication stays in the body. In some cases, this might change the effects and side effects of a medication.
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Baikal skullcap might slow blood clotting. Taking Baikal skullcap along with medications that also slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Sedative medications (CNS depressants)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Baikal skullcap might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Some medications, called sedatives, can also cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking Baikal skullcap with sedative medications might cause breathing problems and/or too much sleepiness.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood pressure: Baikal skullcap might lower blood pressure. Taking it with other supplements that have the same effect might cause blood pressure to drop too much. Examples of supplements with this effect include andrographis, casein peptides, L-arginine, niacin, and stinging nettle.
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar: Baikal skullcap might lower blood sugar. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might lower blood sugar too much. Examples of supplements with this effect include aloe, bitter melon, cassia cinnamon, chromium, and prickly pear cactus.
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Baikal skullcap might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginger, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Herbs and supplements with sedative properties: Baikal skullcap might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking it along with other supplements with similar effects might cause too much sleepiness and/or slowed breathing in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include hops, kava, L-tryptophan, melatonin, and valerian.
Interactions with foods
Products
View all products- Scutellaria baicalensis (Baical skullcap) ext. 300 mg
- Ganoderma lucidum ext. 353 mg
- Lentinula edodes ext. 375 mg
- Perilla frutescens ext. 208 mg
- L-glutamine 3.5 g
- Choline bitartrate 1.5 g
- Retinol palmitate 1.4 mg equiv. vitamin A 750 μg RE
- Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) 12.5 μg equiv. vitamin D 500 IU
- Silybum marianum ext. 86 mg
- Zinc bisglycinate (Zinc amino acid chelate) 30 mg equiv. zinc 6 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Baical skullcap) ext. 200 mg
- Albizia lebbeck ext. 100 mg
- Nigella sativa ext. 100 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 32.13 mg
- Rehmannia glutinosa ext. 42.87 mg
- Plantago asiatica ext. 42.87 mg
- Gentiana scabra ext. 32.13 mg
- Bupleurum falcatum ext. 32.13 mg
- Alisma plantago aquatica ext. 32.13 mg
- Gardenia jasminoides ext. 32.13 mg
- Angelica polymorpha ext. 21.42 mg
- Tetrapanax papyriferus ext. 21.42 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 10.77 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 31.7 mg
- Salvia miltiorrhiza ext. 31.7 mg
- Crataegus pinnatifida ext. 31.7 mg
- Eriobotrya japonica ext. 31.7 mg
- Paeonia obovata ext. 31.7 mg
- Gardenia jasminoides ext. 31.7 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 31.7 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 31.7 mg
- Rehmannia glutinosa ext. 31.7 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 13.19 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 27.96 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 33.54 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 22.35 mg
- Phragmites australis ext. 22.35 mg
- Morus alba ext. 16.77 mg
- Saposhnikovia divaricata ext. 16.77 mg
- Prunus armeniaca ext. 16.77 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 16.77 mg
- Glycine max ext. 16.77 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 11.19 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 11.19 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 9.3 mg
- Platycodon grandiflorus ext. 11.19 mg
- Isatis tinctoria ext. 33.54 mg
- Isatis tinctoria ext. 33.54 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 26.1 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 43.2 mg
- Phragmites australis ext. 34.5 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 34.5 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 26.1 mg
- Prunus armeniaca ext. 26.1 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 26.1 mg
- Fritillaria thunbergii ext. 26.1 mg
- Peucedanum praeruptorum ext. 26.1 mg
- Platycodon grandiflorus ext. 17.4 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 13.8 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 22.387 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 37.312 mg
- Morus alba ext. 37.312 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 37.312 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 29.85 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 22.387 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum ext. 22.387 mg
- Cinnamomum cassia (bark) ext. 22.387 mg
- Anemone altaica ext. 22.387 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 22.387 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 22.2 mg
- Smilax glabra ext. 36.9 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 36.9 mg
- Gardenia jasminoides ext. 29.4 mg
- Plantago asiatica ext. 29.4 mg
- Bassia scoparia ext. 22.2 mg
- Dictamnus dasycarpus ext. 22.2 mg
- Cynanchum stauntonii ext. 22.2 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 22.2 mg
- Sophora flavescens ext. 22.2 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 12 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 22.2 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 20.4 mg
- Atractylodes macrocephala ext. 22.5 mg
- Astragalus membranaceus ext. 27 mg
- Rehmannia glutinosa ext. 22.5 mg
- Morus alba ext. 22.5 mg
- Lycium chinense ext. 22.5 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum ext. 20.4 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 20.4 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 20.4 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 20.4 mg
- Pseudostellaria heterophylla ext. 20.4 mg
- Pueraria lobata ext. 20.4 mg
- Atractylodes lancea ext. 19.8 mg
- Saposhnikovia divaricata ext. 20.4 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. 20.13 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 26.88 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 26.88 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 26.88 mg
- Morus alba ext. 26.88 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 20.16 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 20.16 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum ext. 20.16 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 20.16 mg
- Gardenia jasminoides ext. 20.13 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 20.13 mg
- Ligusticum sinense ext. 20.13 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 11.16 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis (Huang Qin) ext. equiv. dry 102.6 mg
- Rehmannia glutinosa ext. equiv. dry 223.2 mg
- Senna tora ext. equiv. dry 167.4 mg
- Ophiopogon japonicus ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Rubia cordifolia ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Prunella vulgaris ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Uncaria rhyncophylla ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Leonurus sibiricus ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Tribulus terrestris ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Achyranthes bidentata ext. equiv. dry 133.2 mg
- Paeonia suffruticosa ext. equiv. dry 102.6 mg
- Styphnolobium japonicum ext. equiv. dry 102.6 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. equiv. dry 66.6 mg
- Scrophularia ningpoensis ext. equiv. dry 102.6 mg