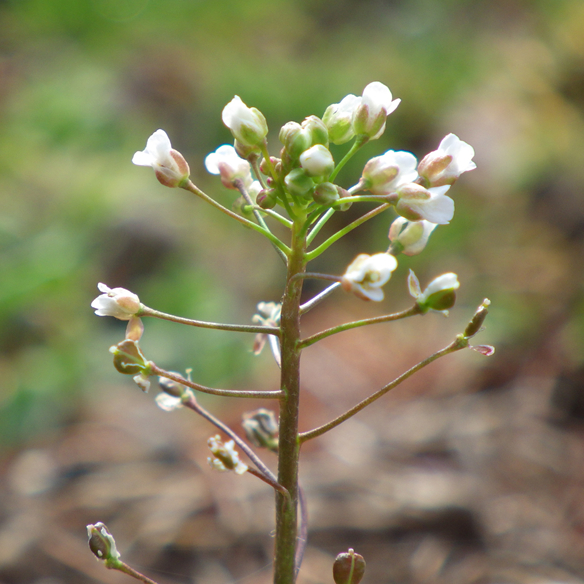
Shepherd's purse
Scientific names: Capsella bursa-pastoris, Thlaspi bursa-pastoris
Family: Brassicaceae/Cruciferae
Alternate names: Blind Weed, Bolsa del Pastor, Bolsa-de-Pastor, Bourse à Berger, Bourse-à-Pasteur, Bourse de Capucin, Boursette, Bursae Pastoris Herba, Capsella, Capselle, Capselle a Pasteur, Capselle Bourse-à-Pasteur, Caseweed, Cocowort, Corne de Lion, Erva-Do-Bom-Pastor, Hirtentaschel, Lady's Purse, Molette de Berger, Mother's-Heart, Moutarde Sauvage, Naeng-i, Pepper-And-Salt, Pick-Pocket, Poor Man's Parmacettie, Rattle Pouches, Sanguinary, Shepherd's Heart, Shepherd's Scrip, Shepherd's Sprout, Shovelweed, St. James' Weed, Tabouret, Tabouret des Champs, Thlaspi, Thlaspi Bourse à Pasteur, Toywort, Witches' Pouches, Zurron de Pastor
Actions: Androgenic activity, Anticarcinogenic, Anti-inflammatory activity, Antimicrobial activity, Antitumor activity, Antiulcer activity, Diuretic activity, Effects on uterine tone, Peroxidase activity, Skin depigmenting
Background
Shepherd's purse is a common weed. It is thought to originate from the Middle East. The parts that grow above the ground are used to make medicine.
Shepherd's purse is used for nosebleeds, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), abnormally heavy bleeding during menstrual periods (menorrhagia), and other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Shepherd's purse is used for nosebleeds, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), abnormally heavy bleeding during menstrual periods (menorrhagia), and other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Shepherd's purse is POSSIBLY SAFE for most adults when taken by mouth in small amounts, short-term. It may cause drowsiness, changes in blood pressure, or changes in thyroid function. Shepherd's purse is POSSIBLY UNSAFE when taken by mouth in large amounts. It can cause heart palpitations.
When applied to the skin: Shepherd's purse is POSSIBLY SAFE when applied to the skin.
Breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if shepherd's purse is safe to use when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Heart conditions: Shepherd's purse might interfere with treatment for heart conditions. It's best to avoid using shepherd's purse if you have a heart condition.
Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis): Shepherd's purse contains chemical compounds called oxalates, which can form kidney stones. If you have had kidney stones in the past, it's best to avoid using shepherd's purse.
Surgery: Shepherd's purse can affect the central nervous system. There is a concern that it might slow down the central nervous system's activity too much when combined with anesthesia and other medications used during and after surgery. Stop using shepherd's purse at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Thyroid conditions: Shepherd's purse might interfere with treatment for thyroid conditions. It's best to avoid using shepherd's purse if you have a thyroid condition.
When applied to the skin: Shepherd's purse is POSSIBLY SAFE when applied to the skin.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy: Shepherd's purse is LIKELY UNSAFE when taken by mouth or applied to the skin during pregnancy. It might cause the uterus to contract or start menstruation, resulting in miscarriage.Breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if shepherd's purse is safe to use when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Heart conditions: Shepherd's purse might interfere with treatment for heart conditions. It's best to avoid using shepherd's purse if you have a heart condition.
Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis): Shepherd's purse contains chemical compounds called oxalates, which can form kidney stones. If you have had kidney stones in the past, it's best to avoid using shepherd's purse.
Surgery: Shepherd's purse can affect the central nervous system. There is a concern that it might slow down the central nervous system's activity too much when combined with anesthesia and other medications used during and after surgery. Stop using shepherd's purse at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Thyroid conditions: Shepherd's purse might interfere with treatment for thyroid conditions. It's best to avoid using shepherd's purse if you have a thyroid condition.
Effectiveness
NatMed Pro rates effectiveness based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Effective, Likely Effective, Possibly Effective, Possibly Ineffective, Likely Ineffective, Ineffective, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate.
Insufficient evidence Effectiveness definitions
- Abnormally heavy bleeding during menstrual periods (menorrhagia). Taking shepherd's purse along with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) may slightly reduce bleeding during a woman's period more than taking an NSAID alone.
- Complications after childbirth. Early research shows that taking shepherd's purse along with oxytocin after childbirth might reduce bleeding more than taking oxytocin alone.
- Headache.
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
- Irregular bleeding between menstrual periods (metrorrhagia).
- Nosebleeds.
- Bleeding from blood vessels (hemorrhage).
- Swelling (inflammation) of the bladder (cystitis).
- Burns.
- Wound healing.
- Bruising.
- Varicose veins.
- Other conditions.
Dosing & administration
The appropriate dose of shepherd's purse depends on several factors such as the user's age, health, and several other conditions. At this time there is not enough scientific information to determine an appropriate range of doses for shepherd's purse. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult your pharmacist or physician or other healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Sedative medications (CNS depressants)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Large amounts of shepherd's purse might cause sleepiness and drowsiness. Medications that cause sleepiness are called sedatives. Taking shepherd's purse along with sedative medications might cause too much sleepiness.
Some sedative medications include clonazepam (Klonopin), lorazepam (Ativan), phenobarbital (Donnatal), zolpidem (Ambien), and others.
Thyroid hormone
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
The body naturally produces thyroid hormone. Shepherd's purse might decrease how much thyroid hormone the body produces. Taking shepherd's purse along with thyroid hormone might decrease the effectiveness of thyroid hormone.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
There are no known interactions with herbs and supplements.
Interactions with foods
There are no known interactions with foods.
Action
Shepherd's purse might decrease bleeding, stimulate muscles, and increase uterine contractions.
Products
View all productsPractitioner product
Per serve:
- Capsella bursapastoris
- Sepia
- Aquilegia vulgaris
- Erigeron canadensis
- Bushmaster snake
- Onosmodium virg
- Oophorinum
- Viburnum opulus
- Porcine ovarian follicle
- Porcine hypothalamus
- Porcine pituitary gland
- Porcine endometrium
- Progesterone
Practitioner product
Discontinued by BioResearch
Practitioner product
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 07/12/2023 11:00:00. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.