The advantages of liposomal technology for nutraceutical delivery
When you prescribe nutritional supplements for your patients, do you find that you must give them large doses to have a therapeutic effect? Conventional nutraceutical delivery systems can be inefficient in delivering a therapeutic dose of any given nutrient to the targeted site - this is where Liposomal technology is revolutionising the administration of drugs and nutraceuticals, ensuring therapeutic doses are delivered directly to target tissues.
There are numerous advantages of using liposomes to deliver the nutrients required by your patients. Most of all, you can be assured that liposomes will provide a therapeutic dose of the nutrient without resorting to an intravenous infusion. The tiny particles are absorbed directly from the mouth into the lymphatic system, bypassing the destructive stomach acid and delivering maximum benefit.
It may seem too good to be true, but liposomes are biocompatible molecules that have been the subject of medical research since the 1970s. Liposomes have been investigated to deliver small molecules such as drugs, proteins, nucleic acids, nutraceuticals, and imaging agents. Their administration is not restricted to oral use. In the medical field, liposomes are used in parenteral, pulmonary, transdermal, ophthalmic, and nasal preparations (1).
Liposomes and cell membranes
Think back to your physiology classes when you learnt about the structure of the cell. Inside the cell, you find the cytoplasm and a collection of essential organelles. Surrounding each cell is the cell membrane.
It consists of two layers of phospholipids arranged tail-to-tail. A phospholipid is a fatty molecule composed of a phosphorylated glycerol hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails (2).
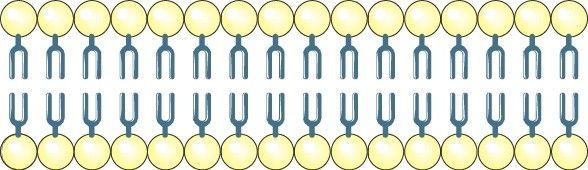
Image 1: The phospholipid cell membrane
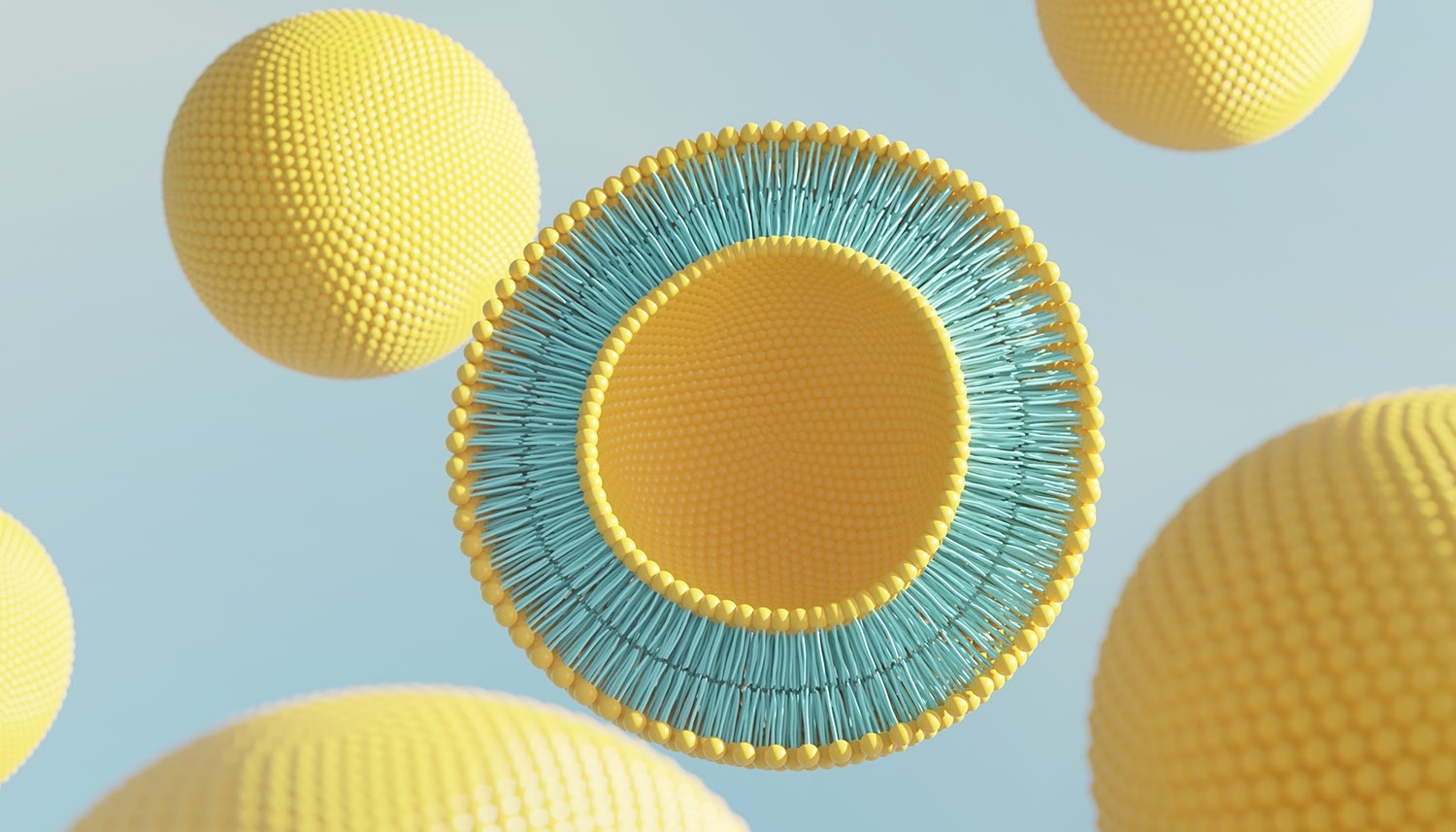
The advantage of using liposomes to deliver nutraceuticals is that they mimic the structure of the cell membrane. The word liposome comes from the words "lipos" (fat) and "soma" (body). A liposome is an artificially formed spherical vesicle made of one or more phospholipid bilayers encapsulating a fluid centre (3).
Size matters
Liposomes range in size from 20 nanometres to 400 nanometres. Research has found that the most effective liposomes are the smallest ones. Smaller molecules are achieved by applying a shear force to the liposomes through various methods, including freeze-thaw cycles, rotor-stator dispersion, sonication, extrusion, and high-pressure homogenisation. Not only are the resulting vesicles smaller, but they also have a more uniform size. The benefits include improved absorption and a longer time in circulation (4).
Liposomal technology for the delivery of nutraceuticals
Conventional nutraceutical delivery systems have many limitations. Pills, tablets and capsules that contain food bioactive ingredients are easy to make, but they are not always the most suitable delivery system. Some nutrients, such as Glutathione, are susceptible to the stomach's acidic environment, so it isn't easy to achieve adequate bioavailability for such products.
Poor solubility, stability and absorption from the digestive tract mean that you must give the patient high doses to have a therapeutic effect (5).
Liposomes offer an alternative nutraceutical delivery system that bypasses the stomach acid and metabolic processes, resulting in large amounts of the bioactive ingredients being destroyed and eliminated before reaching their target.
Liposomes address the problem of poor solubility because water-soluble nutrients such as vitamin C and fat-soluble molecules such as Vitamin D can be encapsulated. The hydrophilic bioactives are trapped in the liposome's aqueous centre, and the hydrophobic molecules are found in the phospholipid membrane (6).
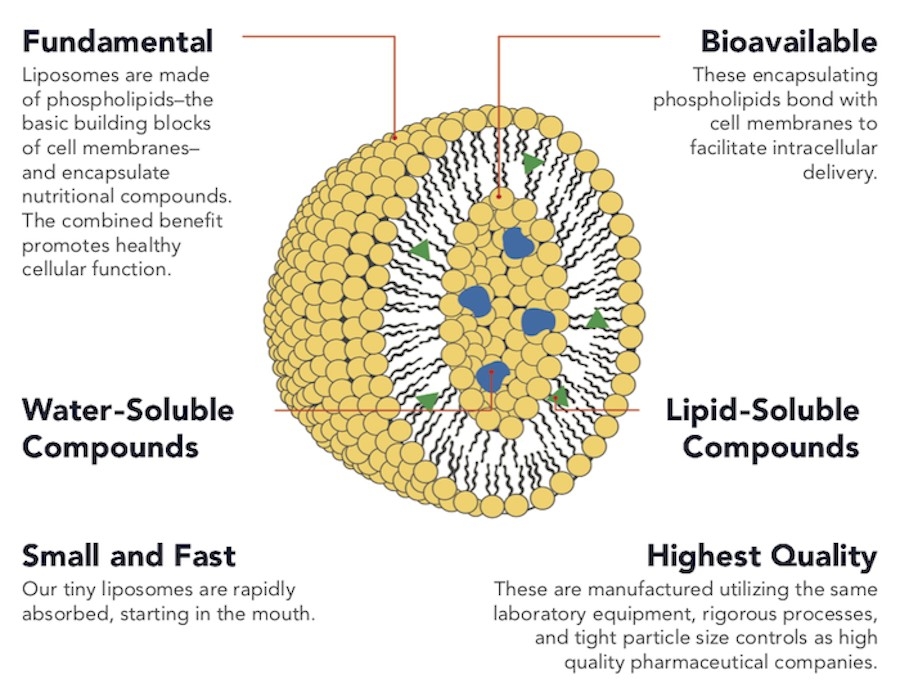
Image 2: Liposome for nutraceutical delivery
Thanks to liposomes' compatibility with the cell wall, once they attach to the cell wall, they can merge with the cell phospholipid bilayer and release the nutrient in the liposome directly into the interior of the cell. In other words, mouth-to-cell absorption.
The effectiveness of liposomes as a nutraceutical delivery vehicle is due to their structure. They share the same structure as our cell membranes. When nutraceuticals are administered with liposomes, it becomes possible to deliver the bioactive compound directly to the target. The liposome's phospholipid membrane attaches to the cell's phospholipid membrane. The two merge, and the bioactive molecules are released directly into the cell (7).
The advantages of liposomal technology for the delivery of nutraceuticals
The authors of an article titled Liposomes for Drug Delivery, published in the Journal of Biotechnology & Biomaterials, listed some of the advantages of using liposomes to deliver medication and nutrients to the body (8):
- Protect the active ingredient from digestion.
- Can carry both water-soluble and fat-soluble molecules.
- Targeted delivery to specific parts of the body.
- Can be used for sustained drug release.
- The size of the molecule can vary according to requirements.
- Lower dosages are required because the active ingredients are not metabolised before entering systemic circulation.
- Compatible with the human body.
- More than one route of administration.
- Reduced risk of taking too much of the active ingredient.
- Greater efficiency.
The goal of an effective nutraceutical delivery system is to deliver the bioactive ingredient to the targeted site, which is what liposomal delivery systems offer.
Liposomes are a revolutionary nutraceutical delivery system that changes how nutrients are administered. It is an effective, accurate and safe method of nutrient administration.
A spotlight on the master antioxidant, Glutathione
The significance of glutathione's potent antioxidant activity is highlighted by its synthesis in every cell cytoplasm in the body .(9) It is considered the most essential endogenous hydrophilic, intracellular antioxidant due to its ability to neutralise lipid peroxides, hydrogen peroxides and reactive oxygen species, regenerate other antioxidants (vitamins C and E), and conjugate and inhibit the oxidative effects of exogenous toxins (9,10).
Why liposomal Glutathione?
Supporting optimal glutathione levels in the (body requires overcoming issues associated with oral glutathione intake, including extensive gastrointestinal hydrolysis and suboptimal bioavailability (9,11).
Combining the biologically active reduced form of oral glutathione (GSH) with liposomal technology provides an effective delivery system specifically designed to overcome these issues by acting as an efficient transport carrier for peptides and proteins (11,12).
Liposomes can enhance the gastrointestinal stability, bioavailability, and absorption of glutathione due to their bilayer structure, with a lipophilic phospholipid layer surrounding a hydrophilic core encapsulating Glutathione (11).
The structural similarity of liposomes to endogenous cell membranes is a key factor in their capacity to improve glutathione bioavailability and absorption, thereby supporting the full spectrum of glutathione's therapeutic benefits in the body (11).
Improving health outcomes with enhanced delivery systems
Here at Designs for Health, we offer a range of liposomal products (Image 3) to support your patients’ needs, including Glutathione for antioxidant support, vitamin C and D for immune support and methyl B12 for nervous system support.
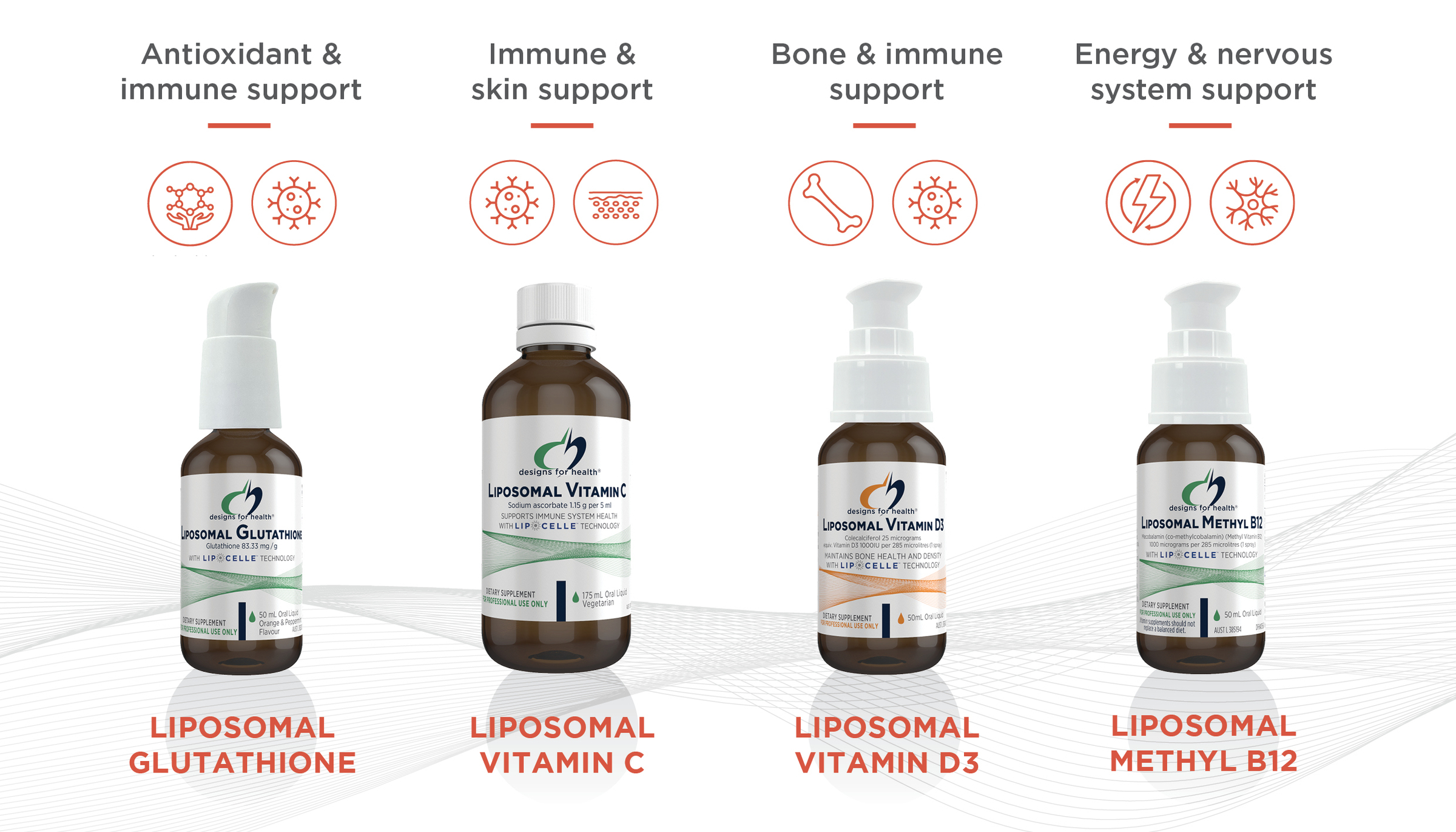
Image 3 – Designs for Health liposomal range
Journey into the future of nutraceutical delivery with liposomal technology and enjoy the benefits of targeted nutrient delivery leading to improved patient compliance and outcomes.